2、RestAPI
2、RestAPI
2.1 导入Demo工程
2.1.1 导入数据
导入课前资料提供的数据库数据:tb_hotel.sql
结构如下:

2.1.2 mapping映射关系
创建索引库,最关键的是mapping映射,而mapping映射要考虑的信息包括:
- 字段名
- 字段数据类型
- 是否参与搜索
- 是否需要分词
- 如果分词,分词器是什么?
其中:
- 字段名、字段数据类型,可以参考数据表结构的名称和类型
- 是否参与搜索要分析业务来判断,例如图片地址,就无需参与搜索
- 是否分词呢要看内容,内容如果是一个整体就无需分词,反之则要分词
- 分词器,我们可以统一使用ik_max_word
由此分析酒店数据的索引库结构为:
PUT /hotel
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}记住一点:在es中做多字段查询时,查询的字段条件越多,效率越低,统计的字段条件越多,效率越低
如何解决?通过copy_to属性将多个字段的信息复制到同一个字段下,
几个特殊字段说明:
- location:地理坐标,里面包含精度、纬度
- all:一个组合字段,其目的是将多字段的值 利用copy_to合并,提供给用户搜索
2.1.3 初始化RestClient
1)引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>2)因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>3)初始化RestHighLevelClient:
初始化的代码如下:
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.204.138:9200")
));将RestHighLevelClient在IOC容器中维护
package cn.itcast.hotel;
@MapperScan("cn.itcast.hotel.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class HotelDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HotelDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient() {
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://192.168.204.138:9200")));
}
}2.2 创建索引库
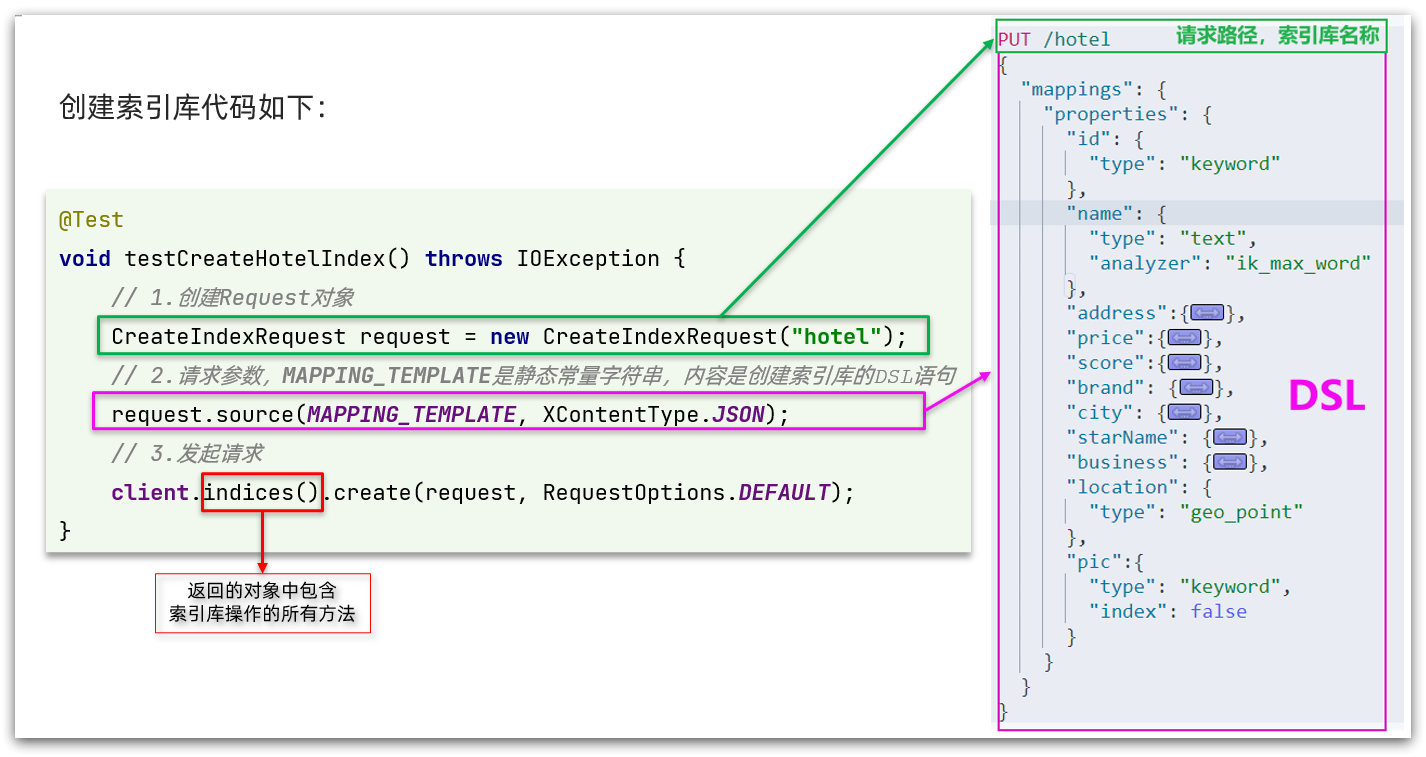
代码分为三步:
- 1)创建Request对象。因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是CreateIndexRequest。
- 2)添加请求参数,其实就是DSL的JSON参数部分。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅。
- 3)发送请求,client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法。
示例:
在hotel-demo的cn.itcast.hotel.constants包下,创建一个类,定义mapping映射的JSON字符串常量:
package cn.itcast.hotel.constants;
public class HotelConstants {
public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"address\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"score\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"city\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"starName\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"business\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"location\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
}测试类:
/**
* 创建索引库
*/
@Test
void testIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建请求对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.设置请求参数 一:DSL语句 二:DSL语句类型
request.source(HotelConstants.MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求 一:请求对象 二:请求配置(默认)
restHighLevelClient.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}2.3 删除索引库
删除索引库的DSL语句非常简单:
DELETE /hotel示例:
/**
* 删除索引库
*/
@Test
void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建请求对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
//2.发送请求
AcknowledgedResponse isSuccess =
restHighLevelClient.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(isSuccess.isAcknowledged()?"删除成功":"删除失败");
}2.4 判断索引库是否存在
判断索引库是否存在,本质就是查询,对应的DSL是:
GET /hotel示例:
/**
* 判断索引库是否存在
*/
@Test
void testExistIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建请求对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
//2.发送请求
Boolean isSuccess = restHighLevelClient.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(isSuccess?"存在":"不存在");
}2.5 总结
JavaRestClient操作elasticsearch的流程基本类似。核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象。
索引库操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是Create、Get、Delete
- 准备DSL( Create时需要,其它是无参)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
